Ambulatory Pharmaceutical Care Clerkship (728-741)
6 Credits
Definition
Ambulatory care pharmacy practice is the provision of integrated, accessible health care services by pharmacists who are accountable for addressing medication needs, developing sustained partnerships with patients, and practicing in the context of family and community. The ambulatory care setting involves interprofessional communication and collaboration to provide acute and chronic patient care that can be accomplished outside the inpatient setting.
Essentials for Practice and Care
The purpose of this course is to emphasize the essentials for practice and care in the ambulatory setting. The essentials for practice and care include providing patient-centered care, managing medication use systems, promoting health and wellness, and describing the influence of population-based care on patient-centered care.
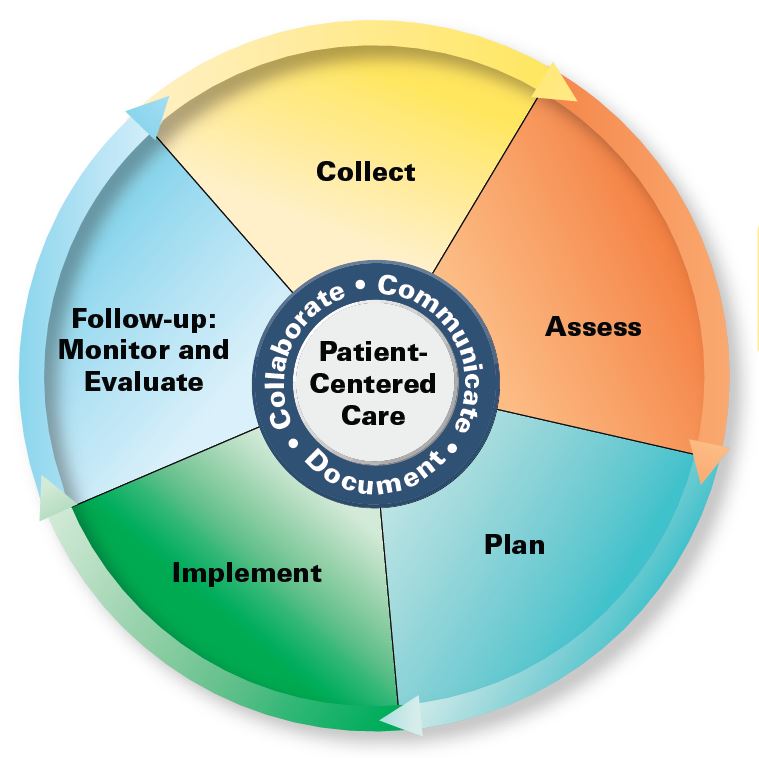
- Patient-centered care – provide patient-centered care as the medication expert (collect and interpret evidence, prioritize, formulate assessments and recommendations, implement, monitor and adjust plans, and document activities).
- Medication use systems management – manage patient healthcare needs using human, financial, technological, and physical resources to optimize the safety and efficacy of medication use systems.
- Health and wellness – design prevention, intervention, and educational strategies for individuals and communities to manage chronic disease and improve health and wellness.
- Population-based care – describe how population-based care influences patient-centered care and the development of practice guidelines and evidence-based best practices.
Approach to Practice and Care
In addition, students will utilize skills when approaching practice and care in the ambulatory setting. These skills include solving problems, education and advocating for patients, collaborating, recognizing social determinants of health, and effectively communicating verbally and nonverbally.
- Problem solving- identify problems; explore and prioritize potential strategies; and design, implement, and evaluate a viable solution.
- Education – educate all audiences by determining the most effective and enduring ways to impart information and assess learning.
- Patient advocacy – represent the patient’s best interests.
- Interprofessional collaboration – actively participate and engage as a healthcare team member by demonstrating mutual respect, understanding, and values to meet patient care needs.
- Cultural sensitivity – recognize social determinants of health to diminish disparities and inequities in access to quality care.
- Communication – effectively communicate verbally and nonverbally when interacting with individuals, groups, and organizations.
Pharmacists’ Patient Care Process – students will provide patient-centered collaborative care as described in the Pharmacists’ Patient Care Process (PPCP) model endorsed by the Joint Commission of Pharmacy Practitioners.